Cell Phones, Cancers and Brain Tumors.
Do cell phones cause Cancer?
What is the REAL story?
Introduction
Cell phones and cancer are in the news all the time now it seems.
But almost everyone uses cell phones. All over the world, tens of
millions of people are pressing them against their heads for hours every
day.
Pew Research Center
says that cell phones are currently used by 97% of
American adults. Worldwide, the
number of cell phone users in 2020 is estimated to be almost 6 billion in
2020 and that number continues to climb (albeit more slowly than in past years as it may be approaching effective saturation).
So what's the fuss? Is cancer caused by cell phones a serious concern, or the media's panic-du-jour?
A cell phone, and a household cordless phone, use a low level form of microwave radiation to send and receive their signals. (see "How do cell phones work" here.) Microwaves, as you know, are used to cook food. As the radiation penetrates tissue it causes it to heat
by vibrating the molecules.
Is this a problem for us with cell phones? That is the current debate. Let's examine the positions and the known evidence, without hype or prejudice. As always, EHSO will provide citations and links to the sources of any evidence provided, so you can verify it for yourself.
Positions, pro and con: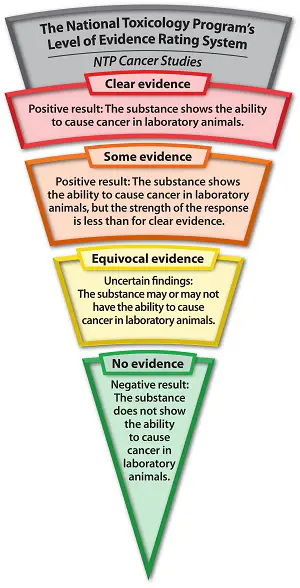
Cell phones are dangerous:
- They emit microwaves.
- They produce heat.
- You hold the source of the emission close to your brain.
- There are claims that people have had brain tumors in the exact size, shape and position as the antenna on their cell phone.
- New 5G phone will use more power and that increases risk
- Recent studies contradict the cell phone industry: In 2018, NTP conducted two-year toxicology studies in rats and mice to help clarify potential health hazards, including cancer risk,
from exposure to RFR like that used in 2G and 3G cell phones which operate within a range of frequencies from about 700–2700 megahertz (MHz). The
NTP studies found that high exposure to RFR (900 MHz) used by cell phones was associated with:
Clear evidence of an association with tumors in
the hearts of male rats. The tumors were malignant schwannomas.
Some
evidence of an association with tumors in the brains of male rats. The tumors were malignant gliomas.
Some evidence of an association with tumors
in the adrenal glands of male rats. The tumors were benign, malignant, or complex combined pheochromocytoma.
Cell phones are safe:
Latest News:
-
February 2020 - US FDA just released results of a review of 125 experiments carried out on animals and 75 on humans between 2008
and August 2019, saying:
"To date, there is no consistent or credible
scientific evidence of health problems caused by the exposure to radio frequency energy emitted by cell phones (see Review of Published Literature between 2008 and 2018 of Relevance to Radiofrequency Radiation and Cancer -
PDF 1.3MB)."
-
March 2019 - A new controversy surface regarding
Bluetooth headsets like Apple's Airpods. See that story here
-
November 2018 - NIH - Cell Phone Radio Frequency Radiation -
Final reports from the rat and mouse studies,
plus the press release
and fact sheet
.
The National Toxicology Program (NTP) concluded there is
clear evidence that male rats exposed to high levels of radio frequency
radiation (RFR) like that used in 2G and 3G cell phones developed
cancerous heart tumors, according to final reports released today. There
was also some evidence of tumors in the brain and adrenal gland of
exposed male rats. For female rats, and male and female mice, the
evidence was equivocal as to whether cancers observed were associated
with exposure to RFR. The final reports represent the consensus of NTP
and a panel of external scientific experts who reviewed the studies in
March after draft reports were issued in February. “The exposures
used in the studies cannot be compared directly to the exposure that
humans experience when using a cell phone,” said John Bucher, Ph.D., NTP
senior scientist. “In our studies, rats and mice received radio
frequency radiation across their whole bodies. By contrast, people are
mostly exposed in specific local tissues close to where they hold the
phone. In addition, the exposure levels and durations in our studies
were greater than what people experience.”
- November 2018 -
Wall Street Journal -
Scientists Find ‘Clear Evidence’ Cellphone Radiation Can Cause Cancer in
Rats.
Researchers cite growing confidence in links between radiation
exposure and some tumors in rats. U.S. researchers found “clear
evidence” that cellphone radiation exposure can cause cancerous heart
tumors in male rats. It is still unclear what the final conclusions of
their two-decades-long study of the health impact on rodents mean for
humans.
-
November 2018 -
NY Times - Study of Cellphone Risks Finds ‘Some Evidence’ of Link to
Cancer, at Least in Male Rats. Many caveats apply, and the results
involve radio frequencies long out of routine use.
-
November 2018 -
NBC News - HEALTH NEWS Cellphone radiation may cause cancer in rats,
report finds. “We agree that these findings should not be applied to
human cell phone usage,” the FDA said.
-
February 2018 -
Consumer Reports - Government Study Suggests Cell Phones May Cause
Cancer in Rats. While the risks are still not clear, here’s our advice
for playing it safe By Jeneen Interlandi February 03, 2018
-
March 2018 -
Scientific American - Does cell phone radiation cause cancer? New
studies show a correlation in lab rats, but the evidence may not resolve
ongoing debates over causality or whether any effects arise in people.
Studies, Facts and Evidence
What is the radiation produced by a cell phone?
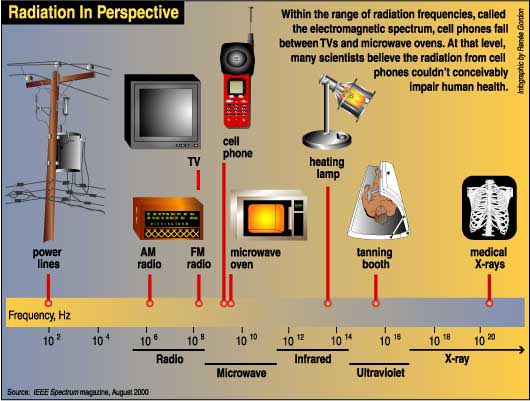
Like televisions, alarm systems, computers, and all other electrical devices, Cell phones (also called mobile phones) are radio devices that use Radiofrequency (Rf) energy emit electromagnetic radiation. They operate at low power (less than 1 watt) by transmitting and receiving electromagnetic radiation in the radiofrequency (RF) end of the spectrum. Radiation which is called "ionizing" can be absorbed by tissue and break molecules apart, such as gamma rays and x-rays, are known to cause cancer. The concern is that the cell phone and it's antenna (the source of the radiation) are held close against the head)

The damage to the dna molecules is thought to be the cause. The radiation that a cell phone uses is also part of the same electromagnetic spectrum, but is not ionizing. For this reason, the US FDA can regulate these devices to ensure that the radiation doesn't pose a health hazard to users, but only once the existence of a public health hazard has been established. (See "It's Not a Food or Medical Product, So Why FDA?") , RF energy was mistakenly thought to similarly cause cancer.
Power
Newer phones are digital. The older analog phones are expected to be phased out by 2006. The major difference is that analog phones use much more power than digital. Analog use about 1.3 Watts, while a digital mobile phone is designed to operate at a maximum power level of 0.6 watts (see http://www.telecom.globalsources.com/MAGAZINE/TS/0209/PANALOG.HTM By comparison, a household microwave oven uses between 600 and 1,100 watts.
Frequency
In the United States, mobile phones operate in a frequency ranging from about 850 to 1900 megahertz (MHz). In that range, the radiation produced is in the form of non-ionizing radiofrequency (RF) energy. This RF energy is different than the ionizing radiation like that from a medical x-ray, which can present a health risk at certain doses.
Ionizing gamma rays and x-rays can cause cancer when their energy is absorbed by the tissue and chemical bonds are broken, damaging DNA. RF energy, on the other hand, produces heating of tissue. Although there is a small amount of experimental evidence that suggests RF energy can impact DNA in rats, this data has been contradicted by several other animal studies and is not well substantiated. Even if true, the doses administered in these animal studies were much larger than the exposure in humans and may have no relevance to cell phone use at all. So although the RF energy emitted by cell phones is in the electromagnetic spectrum, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation can cause cancer, RF energy is very different and has not been shown to cause cancer.
At high enough levels, RF energy, too, can be harmful, because of its ability to heat living tissue to the point of causing biological damage. In a microwave oven, it's RF energy that cooks the food, but the heat generated by cell phones is small in comparison.
A mobile phone's main source of RF energy is its antenna, so the closer the antenna is to a phone user's head, the greater the person's expected exposure to RF energy.
Because RF energy from a cell phone falls off quickly as distance increases between a person and the radiation source (actually, by the distance squared), the safety of mobile phones with an antenna mounted away from the user, like on the outside of a car, has been presumed to be safe. The distance and the effect of the car acting as a Gaussian cage would virtually eliminate the radiation inside the car. Also not presently in doubt is the safety of those so-called cordless phones that have a base unit attached to a home's telephone wiring and operate at much lower power levels than cell phones.
Many experts say that no matter how near the cell phone's antenna--even if it's right up against the skull--the six-tenths of a watt (typically) of power emitted couldn't possibly affect human health.
Scientific Studies to Date
Some mobile phone users have been diagnosed with brain cancer, and many others who have not used mobile phones have gotten the disease, too. Each year in the United States, brain cancer occurs at a rate of about six new cases per 100,000 people. Among the 100 million Americans who own mobile phones, then, about 6,000 cases of brain cancer would be expected among them in a year, even if they had not used mobile phones.
Scientific studies have focused on the question of whether the statistical risk of getting brain cancer is increased in those who use mobile phones compared to non-users, leaving to the courts the judgment of whether Chris Newman or other individuals would have gotten the disease had they not used a cell phone.
Two types of studies are generally used to investigate suspected cancer causes: epidemiological studies, which look at the incidence of a disease in certain groups of people, and animal studies.
This fact sheet from the National Institute of Cancer provides
references to more studies.
Epidemiological studies are sometimes difficult to carry out in a way that can determine whether a cause-and-effect relationship exists between a single variable in a person's life (in this case, cell phone use) and the person's disease (brain cancer). Some factors that complicate research into the asserted link between cell phones and brain cancer: Brain cancer can take years or even decades to develop, making possible long-term effects of mobile phone use difficult to study; mobile phone technology is ever-evolving; and so many lifestyle factors--even down to the precise position in which a person holds the phone, as well as his or her own anatomy--can affect the extent of radiation exposure.
Studies in animals are easier to control, but entail complications of their own. For example, how should results obtained in rats and mice be interpreted in terms of human health risks? And how can scientists account for the fact that these studies sometimes expose animals to RF almost continuously--up to 22 hours a day--and to whole-body radiation, unlike people's head-only exposure?
While studies generally have shown no link between cell phones and brain cancer, there is some conflicting scientific evidence that may be worth additional study, according to FDA. (See "Studies"). The FDA says on their website that they are closely following ongoing research into whether there might be any association between cell phones and cancer.
A long-term study begun in 1994 by the government's National Cancer Institute is already under way to examine possible risk factors for brain cancer. It compares past usage of mobile phones (as well as other environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors) by 800 people with brain tumors compared with 800 others who don't have tumors.
The study, the first part of which is expected to be published early next year, will provide a "snapshot" of what the risks from cell phones could be, says Peter Inskip, Sc.D., one of the study's principal investigators. But this research, he cautions, has its own limitations. For one thing, the study was started in 1994 and it considers radiation exposures from cell phones that occurred between the mid-1980s and 1998. That time frame in large part predates the explosion in the popularity of cell phones, as well as the introduction of digital phones that work on a fraction of the energy compared with older analog varieties.
Recently, FDA announced that it will collaborate with the Cellular Telecommunications Industry Association (CTIA) on additional laboratory and human studies of mobile phone safety. A "Cooperative Research and Development Agreement" signed in June provides for research to be conducted by third parties, with industry funding and FDA oversight to help ensure the studies' quality.
Specifically, FDA will identify the scientific questions that merit attention, propose research to address those questions, review study proposals from those interested in doing the research, make recommendations on the selection of researchers, and oversee the development of study design. Once research is begun, FDA will review the progress of ongoing studies, review the results of completed studies, and issue a report to the CTIA.
Beyond this planned research, according to the industry association, there are hundreds of scientific studies completed or in progress around the world to investigate RF's possible health effects, with half of them specifically addressing the frequencies used by wireless phones. FDA is a leading participant in the World Health Organization's International EMF (electric and magnetic fields) project to coordinate research and the harmonization of international radiation standards.
Ziff-Davis reports that researchers in Australia have reported their hypothesis that normal mobile phone use can lead to cancer. The research group, lead by radiation expert Dr Peter French, principal scientific officer at the Centre for Immunology Research at St Vincent's Hospital in Sydney, said that mobile phone frequencies well below current safety levels could stress cells in a way that has been shown to increased susceptibility to cancer.
The paper, published in the June 2001 issue of the science journal, "Differentiation", says that repeated exposure to mobile phone radiation acts as a repetitive stress, leading to continuous manufacture of heat shock proteins within cells.
Their theory is that these proteins, which are sensitive to heat, are always present in cells at a low level, but are manufactured in larger amounts when the cell is stressed by heat or other environmental factors. These proteins repair other proteins that are adversely affected by the conditions, and are part of the cell's normal reaction to stress. However, if they are produced too often or for too long, they are known to initiate cancer and increase resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
However, this group has reported absolutely evidence nor studies to substantiate this - it is only a theory.
More recently, a Finnish survey of some of the world's most popular mobile phones found the amount of radiation they emit is well below agreed limits and largely in line with data published by manufacturers. The survey conducted by Finland's Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority (STUK) covered 16 new models made by top handset makers including Finland's own Nokia, Motorola of the United States and South Korea's Samsung Electronics. At this level, the study found that head tissue does not warm significantly and no other harmful effects have been proved scientifically. STUK said the SAR levels in all the 28 models tested so far ranged from 0.45 to 1.12 watts per kilogram.
"It is important that also in the future the limits set for radiation from mobile phones and base stations are based on current and confirmed scientific proof of the effects of radiation on health," Kari Jokela, a researcher at STUK, said in a statement. STUK also said that some of its studies have indicated that microwave radiation from mobile phones may cause small changes in how cells operate, but the findings were insufficient for concluding what effects of this radiation had on health. STUK will start testing third-generation UMTS-standard mobile phones during 2005, focusing on the most popular models. Other phones in the current study were made by Sony Ericsson and Siemens.
Finally, as the non-ionizing radiation does have a small heating effect, it is postulated that the effect would be greatest on the eyes and testes, due to the lower amount of blood vessels to help cool these areas.
Perceptions and Concerns
The latest studies may support the generally held position that cell phone radiation is not a substantial hazard, but they will never be able to prove cell phones to be absolutely safe. It is logically impossible to prove a negative, that cell phones can not cause cancer.
Conclusions
There still
mounting credible evidence that cell phones cause cancer or brain tumors
in mammals, especially in test
animals, like mice and rats. Common sense suggests taking reasonable precautions
(see below) . Still it is not time to jump off the deep end, the link between mobile-phone use and cancer is even listed
among the American Cancer Society's
"Top 10 Cancer Myths,"
Cell phones are still relatively new, and while science does not
prove that the radiation may not be likely to cause cancer in humans, time may prove differently! And in any case, it may cause some other type of damage (certainly accidents in cars from being distracted while fumbling with the phone!)
So common sense suggests that we each take some prudent precautions; see
below.
Precautionary Steps To Take
There are some simple steps that cell phone users can take to reduce any remaining risk:
-
First, use earbuds, a headset or speakerphone mode. That moves the phone (and it's antenna) away from your head.
Do not leave the cellphone in your lap, set it on the table next to you.
- Second, consider reserving the use of mobile phones for shorter conversations or when a conventional phone is not available.
- Third, the effects of cellular damage are greatest on growing, developing organisms (i.e., the young), so limit children's use of cell phones!
- Finally, in a car, use an external antenna mounted outside the vehicle to move the source of the radiation farther from you!
And don't believe the claims of conmen preying on people's fear of radiation, selling fraudulent devices that they say protect against radiation. These useless items are mostly sold as "shields" on the Internet. Experts says none of these devices work.
To reduce the risk of an accident while driving, here's a simple tip: enter the several numbers you call the most often in a way that brings them to the top of the list, so you can use fewer keystrokes to dial them. For example, the Motorola V60 starts with an alphabetized list when you press the multi-function button; so start your most commonly called number with "AAA", Like "aaaParents" and the next number with "AAB", like "aabHusband", then they will always appear at the top of the list, which should take fewer keystrokes and less time to dial!
Below are a variety of headsets that will allow you to use your
cellphone without the potential risks of having the transmitter close to
your ear. The Bluetooth versions work with any mobile phone that is
Bluetooth enabled, which includes Apple iPhones and most Android and
smartphones. If your phone does not have Bluetooth, one of the wired
versions will work just the same. If you play music from your
phone, there are stereo headset versions that work both as a headset for
talking on the phone and for playing music. These below have the highest
customer satisfaction for both safety, reliability and voice / sound
quality:
Apple AirPods (Most recent, 3rd Gen) Wireless Ear Buds, Bluetooth Headphones, Sweat and Water Resistant, Long Battery Life
Air Purifiers for Home Large Room Bedroom Up to 1110 Ft² with Air Quality and Light Sensors, Smart WiFi, Washable Filters, HEPA Filter for Pets, Allergy, Dust
Epidemiological and animal studies undertaken by the U.S. cell phone industry and others have yielded mixed results.
- August 2021 -
Effects of mobile phone radiofrequency radiation on sperm quality, Cambridge University Press,
Romualdo Sciorio, Luca Tramontano and Sandro
C. Esteves
-
Scientific American - Major Cell Phone Radiation Study Reignites Cancer Questions, May 27, 2016 - Exposure to radio-frequency radiation linked to tumor formation in
rats
By Dina Fine Maron
-
National Cancer Institute Statement: International Study Shows No
Increased Risk of Brain Tumors from Cell Phone Use - May 17, 2010
- Interphone, an international collaboration, and the largest study of
its kind to date, reported that overall, cell phone users have no
increased risk of two of the most common forms of brain cancer -- glioma
and meningioma. Furthermore, there was no evidence of risk with
progressively increasing number of calls, longer call time, or time
since the start of the use of cell phones. However, for the small
proportion of study participants who used cell phones the most "
measured as cumulative call time over their lifetime " there was a
suggestion of increased risk of glioma, though the authors call this
finding inconclusive. The study was published online May 17, 2010, in
the International Journal of Epidemiology.
-
"No Link Between Cell Phone Use and Brain Tumors" - 12 Apr 2005. A new study has found no link between use of cell phones and the risk of developing a brain tumor. The study is published in the April 12 issue of Neurology, the scientific journal of the American Academy of Neurology.. The Danish study questioned 427 people with brain tumors and 822 people without brain tumors about their cell phone use. The study found no increased risk for brain tumors related to cell phone use, frequency of use, or number of years of use.
- Finnish Study: February 2005: The amount of radiation most popular cell phones emit is well below agreed limits and largely in line with data published by manufacturers. The survey conducted by Finland's Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority (STUK) covered 16 new models made by top handset makers including Finland's own Nokia, Motorola of the United States and South Korea's Samsung Electronics. At this level, the study found that head tissue does not warm significantly and no other harmful effects have been proved scientifically.
- Video interviews with American Cancer Society
, and other researchers.
- Orebro, Sweden, 1999: No connection: In a study published in 1999, investigators at the Orebro Medical Centre in Sweden compared the past mobile phone use of 209 Swedish brain tumor patients and 425 healthy people. Conclusion: The study found no mobile phone/brain cancer link "in virtually all respects," cancer researcher John E. Moulder, Ph.D., says in the August 2000 issue of IEEE Spectrum, the official magazine of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Investigators did find that mobile phone users who got certain types of brain tumors tended to report using the phone on the side of the head where they developed the tumor. The study's limitations, according to Moulder, include a weak association between cell phone use and tumor development, as well as a possibility that the cancer patients' recollections were biased by already knowing on which side of their head the brain cancer developed.
- Joshua Muscat, 1999: Glioma: In a yet-unpublished study presented at a 1999 scientific meeting, researcher Joshua Muscat looked for an association between mobile phone use and a type of brain cancer called glioma. Muscat did not find evidence that cell phone use increased people's risk of this type of brain cancer generally. He did, however, observe an increase in one rare kind of glioma, which FDA scientists say might have occurred by chance. Interestingly, with increased hours of mobile phone use, the risk tended to decrease rather than increase as might be expected.
- A few animal studies have suggested that low levels of RF exposure could speed up development of cancer in laboratory animals. In one recent Australian study, for example, mice genetically altered to be predisposed to developing lymphoma got more than twice as many of these cancers when exposed to RF energy compared to mice not exposed to the radiation.
- A large number of laboratory tests have been conducted to assess RF's effects on genetic material, looking for mutations, chromosomal changes, DNA strand breaks, and structural changes in blood cells' genetic material. One kind of test, called a micronucleus assay, showed structural changes in genetic material after exposure to simulated cell phone radiation. The changes occurred only after 24 hours of continuous exposure, which experts say raises questions about this test's sensitivity to heating effects and whether that sensitivity could be solely responsible for the results.
More Information
Follow-up with:
Agencies
More cell phone usage tumor and cancer news, studies and articles
- November 1, 2018 - National Toxicology Program releases final reports on rat and mouse studies of radio frequency radiation like that used in 2G and 3G cell phone technologies. The
National Toxicology Program (NTP) concluded there is clear evidence that male rats exposed to high levels of radio frequency radiation (RFR)
like that used in 2G and 3G cell phones developed cancerous heart tumors, according to final reports released today. There was also some
evidence of tumors in the brain and adrenal gland of exposed male rats. For female rats, and male and female mice, the evidence was equivocal as
to whether cancers observed were associated with exposure to RFR.
-
May 2016 - A
National Toxicology Program study
conducted on rats found "low incidences" of
two types of tumors in male rats that were exposed to the type of radio
frequencies that are commonly emitted by cellphones. The tumors were
gliomas, which are in the glial cells of the brain, and schwannomas of
the heart.
-
April 2016 -
Has the incidence of brain cancer risen in Australia since the introduction of mobile phones 29 years ago?
- This study says there is no increase in cancers
due to cell phone use. "
"Mobile phone use in Australia began in
1987. Use is now over 90%.
Brain cancer incidence between 1982 and
2013 has not increased in any age group except those aged 70 84; in the
latter group the increase began in 1982, before mobile phones were
introduced.
We hypothesize the increases in incidence of brain
cancer in the oldest age group are due to improved diagnostic detection.
We found no increase in brain cancer incidence compatible with the
steep increase in mobile phone use"
-
2016 - NIH; Researchers from Poland found
that lifestyle factors including stress and mobile phone use can cause human sperm DNA damages. Cell phone use for more than
10 years is found to be positively associated with percentage of immature sperms.
-
August 2014 - WebMD, Medscape Medical News:
Children Face Higher Health Risk From Cell Phones, The potential
harm from microwave radiation (MWR) given off by wireless devices,
particularly for children and unborn babies, is the highlight of a new
review.Although the data are conflicting, links between MWR and cancer
have been observed.
-
June 2012 - Consumer Reports - Consumer Reports did not
conduct any research themselves, but their June 2012 Electronics Buying
Guide, page103, surveyed the research, as we do, and concluded, as we
do, that there still is no clear consensus, and that use of a headset or
speakerphone mode (held away from your head) is prudent.
-
October 21, 2011 -
Largest Study Ever on Cell Phones and Cancer Finds No Link - The
biggest study to look for any connection has found no link between cell
phones and cancer. It followed more than 358,000 people for 13 years and
concluded heavy cell phone users have the same cancer rates as
people who don't use cell phones. The study, out of Denmark, confirms a
smaller one reported on last year. It also contradicts the WHO-IARC
study and confirms the assessments of
the Food and Drug Administration and the Federal Communications
Commission.
-
May 31, 2011 -
WHO
(World Health Organization) IARC just announced that radiation from cell
phones can possibly cause cancer, as reported by CNN. The agency now
lists mobile phone use in the same "carcinogenic hazard" category as
lead, engine exhaust and chloroform. Note that this is a reversal of
WHO's previous position. According to CNN, the Apple iPhone 4 safety
manual warns users, "When using iPhone near your body for voice calls or
for wireless data transmission over a cellular network, keep iPhone at
least 15 mm (5/8 inch) away from the body." and Blackberry Bold advises
users to, "keep the BlackBerry device at least 0.98 in. (25 mm) from
your body when the BlackBerry device is transmitting."
See this page for the IARC's page on the subject.
-
February 22, 2011 -
Cell Phone Calls Alter Brain Activity, Scientists Say; Fox News,
Reuters. Spending 50 minutes with a cellphone plastered to your ear is enough to change
brain cell activity in the part of the brain closest to the antenna. But whether that causes any harm is not clear,
scientists at the
National Institutes of Health said on Tuesday, adding that the study will
likely not settle recurring concerns of a link between cellphones and
brain cancer.
-
May 17, 2010 -
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer
(funded in part by WHO, the World Health
Organization) using a cell phone for as little as 30 minutes
may increase your risk of getting a brain tumor
(glioma). The study is reported to have included 13,000 participants
over 10 years. But we have not seen
the details of this study. As soon as we find a source, we'll publish a
link to it.
-
March 03, 2010 - Yahoo News and CNN reports that
Maine may require a warning about cell phones being a possible cause of
brain cancer. Dr. Derva Davis Mt Sinai Medical center, and Dr. David
Carpenter Albany University spoke in favor of the proposed bill.
-
January 2010: Cell Phones may protect against Alzheimer's. Study
by Dr. Gary Arendash at the Florida Alzheimer's Disease Research Center.
For the complete story, see
Business Week's report or
Fox News report.
-
December 04, 2009:
USA Today: Four-country study finds no cancer link to cellphone usage.
Researchers in four Scandinavian countries found no increase in brain
tumor diagnoses from 1998 to 2003 in a large new study, the latest to
find no link between rising cellphone use and rates of brain cancer.
-
October 13, 2009 -
Mobile Phone Use and Risk of Tumors: A Meta-Analysis - by Seung-Kwon
Myung, Woong Ju, Diana D. McDonnell, Yeon Ji Lee, Gene Kazinets, Chih-Tao
Cheng,
and Joel M. Moskowitz
-
March 30, 2008 - 'Mobile phones 'more dangerous than smoking
' - A
self-published and non-peer reviewed meta-study by Dr. Vini
Khurana, an Australian neurosurgeon, presented an "increasing body of
evidence ... for a link between mobile phone usage and certain brain
tumours" and that it "is anticipated that this danger has far broader
public health ramifications than asbestos and smoking". On
Larry King, on May 27, 2008
, Dr. Khurana said: "the concern is not just brain
tumors, but other health effects associated or reported to be associated
with cell phones, including behavioral disturbances, salivary gland
tumors, male infertility and microwave sickness syndrome".
However, according to Wikipedia, this was criticized as ‘…an unbalanced
analysis of the literature, which is also selective in support of the
author's claims.'
-
February 2008: Tokyo Women's Medical University
compared phone use in 322 brain
cancer patients with 683 healthy people and found that regularly using a
mobile did not significantly affect the likelihood of getting brain
cancer. "Using our newly developed and more accurate techniques, we
found no association between mobile phone use and cancer, providing more
evidence to suggest they don't cause brain cancer," Naohito Yamaguchi,
who led the research, said. His team's findings were published in the
British Journal of Cancer.
- December 5, 2006 - Scientists in Denmark tracked over 420,000 cell phone users over the course of 21 years in an attempt to determine if if cell phone use causes cancer. As reported in ABC News, they found the RF energy produced by the phones did not correlate to an increased incidence of the disease. From the article: 'This so-called Danish cohort "is probably the strongest study out there because of the outstanding registries they keep,' said Joshua Muscat of Pennsylvania State University, who also has studied cell phones and cancer. 'As the body of evidence accumulates, people can become more reassured that these devices are safe, but the final word is not there yet,' Muscat added."
- April 2006 - the Swedish National Institute for Working Life issued a report this week, published in the International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, disputing two earlier studies that claimed cell phone use has no correlation to increased brain tumor risk. The researchers examined the cell phone usage of 905 adults who developed malignant brain tumors. They found that people with more than 2,000 hours of total talk time had 3.7 times the risk of developing brain cancer when compared with nonusers. 2,000 hours is about an hour of talk time every Monday through Friday for 10 years. The study, also found a 2 times increase for tumors specifically on the side of the head where the cell phone was generally used. But it should be noted that the study relied on the memory of the subjects for how long they used their phones, for as much as a decade ago, according to a Daily News interview with Dr. Lydia Zablotska, an epidemiologist at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health. "You're interviewing subjects in an era when everyone has a suspicion that cell phones may be harmful," Zablotska said of the study's shortcomings.
- January 2006 - A four-year long British study performed by the London-based Institute of Cancer Research and three British universities found that talking on a cell phone had no effect on tumor rates. The researchers included 966 people with glioma brain tumors and 1,716 healthy respondents. Individuals were questioned on first use, lifetime years of use, cumulative hours of use, and number of calls they made.
- May 17, 2005 -
Swedish Study Finds Cell Phone-Brain Tumor Link - A Swedish study
finds that users of digital phones in rural areas may be at greater risk
of brain cancer. Its authors say the link is troubling, although they
acknowledge that the amount of data is small and wider research is
needed to amplify the findings. The chance of developing a malignant
brain tumor was roughly eight times higher for cell phone users in the
Swedish countryside than in urban areas. The risk of developing any
brain tumor was four times higher for country dwellers using mobile
phones for five years or more, compared with those who did not use the
devices. The BBC present a program (Panarama) which countered Dr
Lennart Hardell's claims (see this page on the BBC website
), " The National Radiological
Protection Board (NRPB), which advises the government on safety levels,
said the study "the study did not involve enough people to offer
compelling evidence, and any difference in risk it did find was not
statistically significant. . "
- March 21, 2005 - Fox news and CNN News both report that on March 16, 2005, a federal appeals court in Maryland reinstated five class-action lawsuits that allege that the cell phone industry has failed to protect consumers from unsafe levels of radiation. Fox quotes a Dr. Henry Lai, a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, as saying that electromagnetic radiation emitted from cell phones may damage DNA and cause benign brain tumors. Dr. Lai also agrees with EHSO's recommendation to use a headset to minimize potential exposure.
-
Study: Cell phones pose no cancer risk Long-term research still needed, scientists say - MSNBC - The Associated Press - Jan.14, 2004 - LONDON - There is no evidence linking mobile phones to cancer or other health problems, but more research needs to be done to be sure, a panel of experts said Wednesday. The scientists, who are advising the British government, said existing research into the health effects of cell phones “does not give cause for concern” that the devices cause cancer “nor any other adverse health effect.”
- Cell Phone Suit Gets Bad Reception - Friday, October 04, 2002 - Fox News
- Cell Phones Don't Cause Cancer, Rat Study Finds -Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, June 25, 2002 " Radiation from cell phones doesn't appear to cause cancer in rats, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The research team exposed rats to the two most common types of cell phone radiation for four hours a day, five days a week for two years. “We tried to mimic a high level of exposure that humans might experience,” says study leader Joseph L. Roti Roti, Ph.D., professor of radiation oncology, of biochemistry and molecular biophysics and of cell biology and physiology. “We found no statistically significant increases in any tumor type, including brain, liver, lung or kidney, compared to the control group.”
- "No Association Found Between Cellular Phone Use and Risk of Brain Tumors."- National Cancer Institute - 12-21-2000 - Researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) found that people who used cellular phones did not have an increased risk of brain tumors compared to non-users. The study, due to be published in the Jan. 11, 2001, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM)*, was released on Dec. 19, 2000.
- Questions and Answers for the National Cancer Institute Study of Brain Tumors and Use of Cellular Telephones - National Cancer Institute - 12-21-2000 - The results pertain primarily to patterns of cell phone use in the United States during the early to middle 1990s. During the period of this study, there was no evidence that use of hand-held cellular phones caused tumors of the brain and nervous system. The findings suggest that, if there was any increase in risk, it was small, particularly for malignant tumors (glioma).
-
Cell phones increase convenience, but are they really safe? - Spring 2001 - Berkley Medical Journal
- Cell Phones and Brain Tumors - ABC News - May 29, 2001 - A Neurosurgeon's Thoughts - a recent report from the General Accounting Office found that federal agencies do not always provide the latest information and research on cell phone radiation to consumers, and often the information they do provide is too technical for the average consumer to fully understand. Dr. Ted Schwartz, a neurosurgeon from New York Presbyterian Hospital, speaks to the popular concern about the possible connection between cell phones and brain tumors.
- Huge study can't link cancers to cell phones - Danish results add to research that shows no danger - The Associated Press - Wednesday, February 7, 2001 - Scientists who tracked the health of 420,000 Danish cell phone users found no sign the devices increase cancer risk -- the biggest study yet to provide reassurance about the phones' safety, but one that won't end the controversy. The study, published in today's Journal of the National Cancer Institute, found cell phone users are no more likely than anyone else to suffer brain or nervous system cancers, leukemia, or salivary gland tumors.
- Are mobile phones safe? Research intensifies as the public grows wary of one of its favorite communications tools - IEEE Spectrum Online - August 2000 - By Kenneth R. Foster, University of Pennsylvania & John E. Moulder, Medical College of Wisconsin - A MOTORIST USING A WIRELESS TELEPHONE might be worried about having an accident, even while being reassured that if one were to happen, he or she could call for help. Recently some scientists and lay people have expressed alarm at another possible danger--that the use of mobile phones itself may harm the user's health, perhaps even causing cancer.
- Don't get fooled again - USA Today - 08/09/99- Before rushing to judgment, consider the nature of the media and the nature of science. The media essentially created the cell phone scare when CNN's Larry King Live hosted widower David Reynard in 1993. Reynard was suing several phone companies because his wife, who used a cell phone, died of a brain tumor. Reynard and his lawyer didn't have much of what you might call evidence, which is why they didn't get very far in the courts. But the issue has hung around as a media fascination. Television shows and news reports can, in a matter of moments, leave a lasting impression. Science is different. It takes years to collect and analyze data, and that's just for one study
Positions by Authorities...
...that conducted their own research or are credible to offer a meaningful opinion
Cell Phones Are Dangerous
- Note: It has been very difficult to find credible sources that have taken the position that cell phones are dangerous. This may be because this position is unsupportable (like taking the position that the earth is flat) or that there is new evidence that contradicts current thinking (like Copernicus' calculations that the earth revolves around the sun) .
Is the truth being suppressed for financial interests? In an era when we find out the government has admitted to lying about the existence of
UFO's for 70 years, it is difficult to find the truth about many things.
Credible sources means persons of institutions whose education, practice, past performance, and affiliations would lead a logical person to conclude that they are knowledgeable about the subject and have conducted thorough, accurate and unbiased research. If you would like to recommend a source, please
use the feedback form!
-
May 2016 - A
National Toxicology Program study
conducted on rats found "low incidences" of
two types of tumors in male rats that were exposed to the type of radio
frequencies that are commonly emitted by cellphones. The tumors were
gliomas, which are in the glial cells of the brain, and schwannomas of
the heart.
-
2010 - Disconnect: The Truth About Cell Phone Radiation, What the Industry Has Done to Hide It, and How to Protect Your Family -
Dr. Devra Davis is
the founding director of the toxicology and environmental studies board at the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, Cell Phones Pose Health Risks,
-
2010, UC Davis - Heavy
cell-phone use over many years may threaten one’s health, according to well-known environmental activist, cancer epidemiologist, and author
Dr. Devra Davis, MPH, PhD,
- Dr. Mercola - Cell Phones and Cancer He has an extensive website, but he is an an osteopathic physician, not a medical doctor. He also has not conducted any research himself; he just reviewed a study conducted by a television program (20/20) and we have all seen from Dan Rather's performance lately that the news media are not to be trusted as credible sources - they are meant to report the news objectively, not create research.
Cell Phones Do Not Cause Cancer
-
April 2016 -
Has the incidence of brain cancer risen in Australia since the introduction of mobile phones 29 years ago?
- This study says there is no incease in cancers
due to cell phone use.
" Mobile phone use in Australia began in
1987. Use is now over 90%.
Brain cancer incidence between 1982
and 2013 has not increased in any age group except those aged 70 84;
in the latter group the increase began in 1982, before mobile phones
were introduced.
We hypothesize the increases in incidence of
brain cancer in the oldest age group are due to improved diagnostic
detection.
We found no increase in brain cancer incidence
compatible with the steep increase in mobile phone use"
-
Tokyo Women's Medical University
compared phone use in 322 brain cancer patients with
683 healthy people and found that regularly using a mobile did not
significantly affect the likelihood of getting brain cancer. "Using our
newly developed and more accurate techniques, we found no association
between mobile phone use and cancer, providing more evidence to suggest
they don't cause brain cancer," Naohito Yamaguchi, who led the research,
said. His team's findings were published in the British Journal of
Cancer.
-
American Cancer Society - "Considerable research has also found no clear association between any other electronic consumer products and cancer. Cell phones, microwave ovens and related appliances emit low-frequency radiation "the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that includes radio waves and radar. Ionizing radiation such as gamma rays and X-rays can increase cancer risk by causing changes to DNA in cells of the body. Low frequency, non-ionizing radiation does not cause these DNA changes"
- Medical College of Wisconsin - A very detailed page, with a considerable amount of information, including both FAQs and citations to references; it can be technically overwhelming for non scientists.
- National Institute of Health / National Cancer Institute - April 2000. "There was no evidence of higher brain tumor risk among people who use hand-held cellular phones compared to those who do not use them."
- The Independent Expert Group chaired by Sir William Stewart published its report on the health implications of mobile phones in 2000. Two later reports by the independent Advisory Group on Non-ionising Radiation (AGNIR) and the most recent “Mobile Phones and Health 2004” by the National Radiological Protection Board (NRPB), have endorsed Stewart's findings. All three reports can be found at: www.nrpb.org.uk.
Undecided
Additional resources
- For more information, the ACS book, Cancer: What Causes It, What Doesn't provides an educated perspective on what cancer health hazards people may face in everyday life, and what's not worth worrying about.
- American Cancer Society - Environmental Carcinogens - Cellular Phones and Risk of Brain Tumors
- Bioelectromagnetics Society: www.bioelectromagnetics.org
- Britain's report from their Independent Expert Group on Mobile Phones
- Cell Telecommunications and Internet Association
- Council on Wireless Technology Impacts (non government0
- U.S. Dept. of Defense: www.brooks.af.mil/AFRL/HED/hedr/
- European Bioelectromagnetics Association: www.ebea.org
- Electromagnetic Energy Association: www.elecenergy.com
- Federal Communications Commission: www.fcc.gov/oet/rfsafety
- U.S. Food and Drug Administraton: www.fda.gov/cdrh/phones/index.html
- Cell Phones and Brain Tumors - from HoaxInfo.com, April 1, 2001
- ICNIRP (Europe): www.icnirp.de
- IEEE: www.ieee.org
- IEEE Committee on Man & Radiation: www.seas.upenn.edu:8080/~kfoster/comar.htm
- International Electromagnetic Field Conference:www.who.int/peh-emf/
- Microwave News: www.microwavenews.com
- Mobile Manufacturers Forum
- Motorola's information on health and safety
- J.Moulder, Med.Coll.of Wisc.: www.mcw.edu/gcrc/cop/cell-phone-health-FAQ/toc.html
- National Brain Tumor Foundation
- National Council on Radiation Protection & Measurements: www.ncrp.com
- National Institute of Environmental Health Science:www.niehs.nih.gov
- National Radiation Protection Board (United Kingdom): www.nrpb.org.uk
- New England Journal of Medicine - Study on cell telephone use and brain tumors
- NJ Dept Radiation Protection: www.state.nj.us/dep/rpp/ber/nrs/index.htm
- RF Safety Program, Office of Engineering and Technology, Federal Communications Commission:www.fcc.gov/oet/rfsafety/Richard Tell Associates: www.radhaz.com
- United Kingdom, National Radiological Protection Board: www.nrpb.org.uk/Advice/Nir-is4.htm
- US OSHA: www.osha-slc.gov/SLTC/radiofrequencyradiation/index.html
- Wireless Industry (CTIA): www.wow-com.com
- Wireless Consumers Alliance, a non-profit corporation,
- Wireless Information Resource Centre (Canada): www.wirc.org
- World Health Organization (WHO): www.who.ch/peh-emf
FCC and FDA Background Information
FCC Policy on Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields The FCC is required by the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 to evaluate the effect of emissions from FCC-regulated transmitters on the quality of the human environment. At the present time there is no federally-mandated radio frequency (RF) exposure standard. However, several non-government organizations, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE), and the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) have issued recommendations for human exposure to RF electromagnetic fields. The potential hazards associated with RF electromagnetic fields are discussed in OET Bulletin No. 56, "Questions and Answers About the Biological Effects and Potential Hazards of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields." More Info....
The US FCC's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) | |

|
FCC's Radiofrequency Energy FAQs (Updated)
This section contains answers to the most frequently asked questions received by the Federal Communications Commission concerning RF fields and its application. Also, see FCC OET Bulletin No. 56: .
| OET RF Safety Bulletins, Fact Sheets, Guides and Reports | |
 |
OET Bulletin No. 56: Questions and Answers About Biological Effects Potential Hazards of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields (Fourth Edition, August 1999) This is an informative bulletin written as a result of increasing interest and concern of the public with respect to this issue. The expanding use of radio frequency technology has resulted in speculation concerning the alleged "electromagnetic pollution" of the environment and the potential dangers of exposure to non-ionizing radiation. This publication is designed to provide factual information to the public by answering some of the most commonly asked questions. OET Bulletin No. 65: Evaluating Compliance With FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields This technical bulletin was issued to provide guidance in the implementation of the Commission's new exposure limits and policies. The bulletin provides acceptable methods of determining compliance Commission limits through the use of mathematical and empirical models. - Supplement A: Additional Information for Radio and Television Broadcast Stations
- Supplement B: Additional Information for Amateur Radio Stations
- Supplement C: Additional Information for Evaluating Compliance of Mobile and Portable Devices with FCC Limits for Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Emissions
Information on Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Fields from Cellular and PCS Radio Transmitters
This page explains technical information on cellular and PCS base stations, mobile, and portable telephones. (Adobe PDF | WordPerfect 5.1) A Local Government Official's Guide to Transmitting Antenna RF Emission Safety: Rules, Procedures, and Practical Guidance. The LSGAC and the FCC have developed this guide to aid local governmental officials and citizens in understanding safety issues related to radiofrequency emissions from telecommunications towers. [Word97 | Acrobat | News Release]
|  |
That have responsibilities related to potential RF Health effects Certain agencies in the Federal Government have been involved in monitoring, researching or regulating issues related to human exposure to RF radiation. These agencies include the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) and the Department of Defense (DOD). By authority of the Radiation Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968, the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) of the FDA develops performance standards for the emission of radiation from electronic products including X-ray equipment, other medical devices, television sets, microwave ovens, laser products and sunlamps. The CDRH established a product performance standard for microwave ovens in 1971 limiting the amount of RF leakage from ovens. However, the CDRH has not adopted performance standards for other RF-emitting products. The FDA is, however, the lead federal health agency in monitoring the latest research developments and advising other agencies with respect to the safety of RF-emitting products used by the public, such as cellular and PCS phones. The FDA's microwave oven standard is an emission standard (as opposed to an exposure standard) that allows specific levels of microwave leakage (measured at five centimeters from the oven surface). The standard also requires ovens to have two independent interlock systems that prevent the oven from generating microwaves the moment that the latch is released or the door of the oven is opened. The FDA has stated that ovens that meet its standards and are used according to the manufacturer's recommendations are safe for consumer and industrial use. More information is available from: www.fda.gov/cdrh. - The EPA has, in the past, considered developing federal guidelines for public exposure to RF radiation. However, EPA activities related to RF safety and health are presently limited to advisory functions. For example, the EPA now chairs an Inter-agency Radiofrequency Working Group, which coordinates RF health-related activities among the various federal agencies with health or regulatory responsibilities in this area.
- OSHA is responsible for protecting workers from exposure to hazardous chemical and physical agents. In 1971, OSHA issued a protection guide for exposure of workers to RF radiation [29 CFR 1910.97]. However, this guide was later ruled to be only advisory and not mandatory. Moreover, it was based on an earlier RF exposure standard that has now been revised. At the present time, OSHA uses the IEEE and/or FCC exposure guidelines for enforcement purposes under OSHA's "general duty clause" (for more information see: www.osha- slc.gov/SLTC/radiofrequencyradiation/index.html ).
- NIOSH is part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. It conducts research and investigations into issues related to occupational exposure to chemical and physical agents. NIOSH has, in the past, undertaken to develop RF exposure guidelines for workers, but final guidelines were never adopted by the agency. NIOSH conducts safety-related RF studies through its Physical Agents Effects Branch in Cincinnati,Ohio.
- The NTIA is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce and is responsible for authorizing Federal Government use of the RF electromagnetic spectrum. Like the FCC, the NTIA also has NEPA responsibilities and has considered adopting guidelines for evaluating RF exposure from U.S. Government transmitters such as radar and military facilities.
- The Department of Defense (DOD) has conducted research on the biological effects of RF energy for a number of years. This research is now conducted primarily at the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory located at Brooks Air Force Base, Texas. (Back to Index)
For more information on this topic please note: OET Bulletin No. 56: Questions and Answers About the Biological Effects and Potential Hazards of Radiofrequency Radiation. |  |
Information on Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Fields from Cellular and PCS Radio Transmitters
This page explains technical information on cellular and PCS base stations, mobile, and portable telephones. (Adobe PDF | WordPerfect 5.1)
A Local Government Official's Guide to Transmitting Antenna RF Emission Safety: Rules, Procedures, and Practical Guidance. The LSGAC and the FCC have developed this guide to aid local governmental officials and citizens in understanding safety issues related to radiofrequency emissions from telecommunications towers. [Word97 | Acrobat | News Release]
Other Issues


